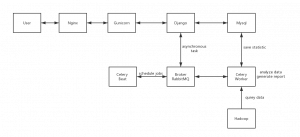
跟第三方平台打交道,经常需要设置一个接受通知的Webhook,比如微信/Skype的回调。它们要求有一个可以在互联网上访问得了的入口,比如某个域名,如果是在本地开发的话,不好调试。通常使用花生壳来代理本地服务,但是花生壳有一些限制,比如端口。有些域名服务商,比如DNSPOD,Linode,提供相应的API,也可以自己搭建DDNS服务,但是也可能有端口访问限制。Frp/Ngrok都是Go语言开发的内网穿透工具,可以自己部署搭建。Frp是国人开发的一款反向代理软件,可以转发请求给位于NAT后面的机器,支持TCP,UDP,HTTP/HTTPS。Ngrok则是国外的一款内网穿透软件,也支持HTTP/HTTPS转发。这里使用Nginx作为反向代理服务器,接收互联网回调并转发给本地的Frp/Ngrok服务,由它们接收webhook请求并转发至本地开发环境。
前面使用OpenVpn搭建了私有网络,可以在Nginx里面配置转发给目标机器就可以了
vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/100-dev.example.conf
内容如下
server {
listen 80;
server_name dev.example.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443;
server_name dev.example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl on;
ssl_session_cache builtin:1000 shared:SSL:10m;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!CAMELLIA:!DES:!MD5:!PSK:!RC4;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_pass http://10.9.0.2/;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
这里使用了let’s encryt的泛域名证书,官方并没有对应的插件,但是DNSPOD有提供相应的API,第三方开发了一个插件自certbot-dns-dnspod,安装这个插件并且配置Dnspod的API Token:
$ yum install certbot python2-certbot-nginx
$ certbot --nginx
$ curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
$ pip install certbot-dns-dnspod
$ vim /etc/letsencrypt/dnspod.conf
certbot_dns_dnspod:dns_dnspod_email = "[email protected]"
certbot_dns_dnspod:dns_dnspod_api_token = "123,ca440********"
$ chmod 600 /etc/letsencrypt/dnspod.conf
手动请求证书
$ certbot certonly -a certbot-dns-dnspod:dns-dnspod --certbot-dns-dnspod:dns-dnspod-credentials /etc/letsencrypt/dnspod.conf --server https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory -d example.com -d "*.example.com"
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
Plugins selected: Authenticator certbot-dns-dnspod:dns-dnspod, Installer None
Starting new HTTPS connection (1): acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org
Obtaining a new certificate
Performing the following challenges:
dns-01 challenge for example.com
dns-01 challenge for example.com
Starting new HTTPS connection (1): dnsapi.cn
Waiting 10 seconds for DNS changes to propagate
Waiting for verification...
Cleaning up challenges
Resetting dropped connection: acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2019-08-04. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot
again. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run
"certbot renew"
*/1 * * * * /usr/local/qcloud/stargate/admin/start.sh > /dev/null 2>&1 &
- If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
$ ls -la /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/
total 12
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 6 12:06 .
drwx------ 3 root root 4096 May 6 12:06 ..
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 34 May 6 12:06 cert.pem -> ../../archive/example.com/cert1.pem
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 35 May 6 12:06 chain.pem -> ../../archive/example.com/chain1.pem
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 39 May 6 12:06 fullchain.pem -> ../../archive/example.com/fullchain1.pem
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 37 May 6 12:06 privkey.pem -> ../../archive/example.com/privkey1.pem
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 692 May 6 12:06 README
配置证书自动更新
0 0,12 * * * python -c 'import random; import time; time.sleep(random.random() * 3600)' && certbot renew
Frp的开发者已经提供了编译好的frp服务端和客户端,下载即可使用。这里使用docker来运行Frp服务,使用这个Dockerfile,更改版本号为0.26.0,并编译
$ docker build . -t frps:0.26
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
frps 0.26 8a87cb91d4de 2 hours ago 21.1MB
测试一下SSH代理服务,创建服务端配置文件
mkdir -p frp/conf
vim frp/conf/frps.ini
frps.ini内容
[common]
bind_port = 7000
运行一下frp服务端
#清除先前运行的容器
$ docker rm frp-server
$ docker run --name frp-server -v /root/frp/conf:/conf -p 7000:7000 -p 6000:6000 frps:0.26
2019/04/22 06:41:17 [I] [service.go:136] frps tcp listen on 0.0.0.0:7000
2019/04/22 06:41:17 [I] [root.go:204] Start frps success
2019/04/22 06:41:27 [I] [service.go:337] client login info: ip [110.87.98.82:61894] version [0.26.0] hostname [] os [linux] arch [386]
2019/04/22 06:41:27 [I] [tcp.go:66] [e8783ecea2085e15] [ssh] tcp proxy listen port [6000]
2019/04/22 06:41:27 [I] [control.go:398] [e8783ecea2085e15] new proxy [ssh] success
2019/04/22 06:41:41 [I] [proxy.go:82] [e8783ecea2085e15] [ssh] get a new work connection: [110.*.*.*:61894]
这里映射了2个端口,端口7000是frp服务端监听的端口,以便客户端能够连接上;端口6000是需要服务端监听这个端口,以便提供反向代理服务,比如SSH。如果使用的是腾讯云,相应的端口需要在安全组放行。
客户端直接下对应的包,里面有配置试例。创建本地配置文件frpc.ini如下
[common]
server_addr = 123.*.*.*
server_port = 7000
[ssh]
type = tcp
local_ip = 127.0.0.1
local_port = 22
remote_port = 6000
这个配置即告诉服务端,将服务端的6000端口转发到本地的22端口。本地运行
$ ./frpc -c ./frpc.ini.ssh
2019/04/22 06:41:27 [I] [service.go:221] login to server success, get run id [e8783ecea2085e15], server udp port [0]
2019/04/22 06:41:27 [I] [proxy_manager.go:137] [e8783ecea2085e15] proxy added: [ssh]
2019/04/22 06:41:27 [I] [control.go:144] [ssh] start proxy success
然后在服务端连接客户端。这里连接的是服务端的6000端口,会被转发给远程(局域网内)主机
[rth@centos72]$ ssh -oPort=6000 vagrant@123.*.*.*
The authenticity of host '[123.*.*.*]:6000 ([123.*.*.*]:6000)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is SHA256:NhBO/PDL***********************.
RSA key fingerprint is MD5:20:70:e2:*:*:*:*:*:*:*:*:*:*:*:*:*.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '[123.*.*.*]:6000' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
vagrant@123.*.*.*'s password:
Last login: Mon Apr 22 06:39:07 2019 from 10.0.2.2
[vagrant@centos64 ~]$ exit
logout
Connection to 123.*.*.* closed.
Frp转发http服务很简单。在conf目录下创建配置frps.ini监听本机来自8080端口的HTTP请求
[common]
bind_port = 7000
vhost_http_port = 8080
[root@VM_1_218_centos frp]# docker run --name frp-server -v /root/frp/conf:/conf -p 7000:7000 -p 8080:8080 frps:0.26
2019/05/06 07:26:28 [I] [service.go:136] frps tcp listen on 0.0.0.0:7000
2019/05/06 07:26:28 [I] [service.go:178] http service listen on 0.0.0.0:8080
2019/05/06 07:26:28 [I] [root.go:204] Start frps success
2019/05/06 07:26:51 [I] [service.go:337] client login info: ip [123.*.*.*:56758] version [0.26.0] hostname [] os [linux] arch [386]
2019/05/06 07:26:51 [I] [http.go:72] [19f60a30aa924343] [web] http proxy listen for host [test.example.com] location []
2019/05/06 07:26:51 [I] [control.go:398] [19f60a30aa924343] new proxy [web] success
2019/05/06 07:27:05 [I] [proxy.go:82] [19f60a30aa924343] [web] get a new work connection: [123.*.*.*:56758]
2019/05/06 07:27:05 [I] [proxy.go:82] [19f60a30aa924343] [web] get a new work connection: [123.*.*.*:56758]
2019/05/06 07:27:06 [I] [proxy.go:82] [19f60a30aa924343] [web] get a new work connection: [123.*.*.*:56758]
然后配置Nginx转发请求
$ vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/100-dev.example.conf
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/;
proxy_redirect off;
}
创建本地web传教客户端配置frpc.ini,将来自服务器dev.example.com:8080端口的HTTP请求转发至本地80端口
[common]
server_addr = 123.*.*.*
server_port = 7000
[web]
type = http
local_port = 80
custom_domains = dev.example.com
运行本地客户端
[root@vagrant-centos64 frp]# ./frpc -c ./frpc.ini
2019/05/06 07:26:51 [I] [service.go:221] login to server success, get run id [19f60a30aa924343], server udp port [0]
2019/05/06 07:26:51 [I] [proxy_manager.go:137] [19f60a30aa924343] proxy added: [web]
2019/05/06 07:26:51 [I] [control.go:144] [web] start proxy success
2019/05/06 07:27:37 [E] [control.go:127] work connection closed, EOF
2019/05/06 07:27:37 [I] [control.go:228] control writer is closing
2019/05/06 07:27:37 [I] [service.go:127] try to reconnect to server...
访问dev.example.com既可以看到本地web服务器页面。Frp还可以代理其他请求,也有在它基础上二次加工提供基于token认证的转发服务。
Ngrok 2.0以后不再开源,只能使用1.3版本的搭建。这里使用docker-ngrok来构建。Ngrok构建需要SSL证书,复制刚才生成的letsencypt证书并更改server.sh
$ git clone https://github.com/hteen/docker-ngrok
$ cp /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem myfiles/base.pem
$ cp /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem myfiles/fullchain.pem
$ cp /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem myfiles/privkey.pem
$ vim server.sh
#!/bin/sh
set -e
if [ "${DOMAIN}" == "**None**" ]; then
echo "Please set DOMAIN"
exit 1
fi
if [ ! -f "${MY_FILES}/bin/ngrokd" ]; then
echo "ngrokd is not build,will be build it now..."
/bin/sh /build.sh
fi
${MY_FILES}/bin/ngrokd -tlsKey=${MY_FILES}/privkey.pem -tlsCrt=${MY_FILES}/fullchain.pem -domain="${DOMAIN}" -httpAddr=${HTTP_ADDR} -httpsAddr=${HTTPS_ADDR} -tunnelAddr=${TUNNEL_ADDR}
构建Ngrok镜像
[root@VM_1_218_centos docker-ngrok]# docker build -t ngrok:1.3 .
[root@VM_1_218_centos docker-ngrok]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
ngrok 1.3 dc70190d6377 13 seconds ago 260MB
frps 0.26 8a87cb91d4de 2 hours ago 21.1MB
alpine latest cdf98d1859c1 12 days ago 5.53MB
然后交叉编译生成Linux/Mac/Windows平台的客户端
$ rm -rf assets/client/tls/ngrokroot.crt
$ cp /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/chain.pem assets/client/tls/ngrokroot.crt
$ rm -rf assets/server/tls/snakeoil.crt
$ cp /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/cert.pem assets/server/tls/snakeoil.crt
$ rm -rf assets/server/tls/snakeoil.key
$ cp /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem assets/server/tls/snakeoil.key
$ GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 make release-client
$ GOOS=windows GOARCH=amd64 make release-client
$ GOOS=darwin GOARCH=amd64 make release-client
在服务器上运行Ngrok服务,将8090端口请求转发给容器的80端口,并且映射容器的4443端口到服务器的7000端口,以便客户端连接
[root@VM_1_218_centos docker-ngrok]# docker run --name ngrok -e DOMAIN='example.com' -p 8090:80 -p 8091:443 -p 7000:4443 -v /root/docker-ngrok/myfiles:/myfiles ngrok:1.3 /bin/sh /server.sh
[09:18:21 UTC 2019/05/07] [INFO] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Info:83) [registry] [tun] No affinity cache specified
[09:18:21 UTC 2019/05/07] [INFO] (ngrok/log.Info:112) Listening for public http connections on [::]:80
[09:18:21 UTC 2019/05/07] [INFO] (ngrok/log.Info:112) Listening for public https connections on [::]:443
[09:18:21 UTC 2019/05/07] [INFO] (ngrok/log.Info:112) Listening for control and proxy connections on [::]:4443
[09:18:21 UTC 2019/05/07] [INFO] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Info:83) [metrics] Reporting every 30 seconds
[09:18:27 UTC 2019/05/07] [INFO] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Info:83) [tun:18e8cd42] New connection from 123.*.*.*:50529
[09:18:27 UTC 2019/05/07] [DEBG] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Debug:79) [tun:18e8cd42] Waiting to read message
[09:18:27 UTC 2019/05/07] [DEBG] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Debug:79) [tun:18e8cd42] Reading message with length: 125
[09:18:27 UTC 2019/05/07] [DEBG] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Debug:79) [tun:18e8cd42] Read message {"Type":"Auth","Payload":{"Version":"2","MmVersion":"1.7","User":"","Password":"","OS":"linux","Arch":"amd64","ClientId":""}}
[09:18:27 UTC 2019/05/07] [INFO] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Info:83) [ctl:18e8cd42] Renamed connection tun:18e8cd42
[09:18:27 UTC 2019/05/07] [INFO] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Info:83) [registry] [ctl] Registered control with id 1957f20b9b3ce3b76c7d8fc8b16276ed
[09:18:27 UTC 2019/05/07] [DEBG] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Debug:79) [ctl:18e8cd42] [1957f20b9b3ce3b76c7d8fc8b16276ed] Writing message: {"Type":"AuthResp","Payload":{"Version":"2","MmVersion":"1.7","ClientId":"1957f20b9b3ce3b76c7d8fc8b16276ed","Error":""}}
[09:18:27 UTC 2019/05/07] [DEBG] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Debug:79) [ctl:18e8cd42] [1957f20b9b3ce3b76c7d8fc8b16276ed] Writing message: {"Type":"ReqProxy","Payload":{}}
[09:18:27 UTC 2019/05/07] [DEBG] (ngrok/log.(*PrefixLogger).Debug:79) [ctl:18e8cd42] [1957f20b9b3ce3b76c7d8fc8b16276ed] Waiting to read message
将刚才编译的客户端下载下来,创建grok.cfg,连接服务器的7000端口
server_addr: "example.com:7000"
trust_host_root_certs: false
指定要监听的域名,及本地web端口
./ngrok -config=ngrok.cfg -subdomain=dev 9010
ngrok (Ctrl+C to quit)
Tunnel Status online
Version 1.7/1.7
Forwarding http://dev.flexkit.cn -> 127.0.0.1:9010
Forwarding https://dev.flexkit.cn -> 127.0.0.1:9010
Web Interface 127.0.0.1:4040
# Conn 2
Avg Conn Time 46.84ms
HTTP Requests
-------------
GET /teams 200 OK
请求dev.example.com即可以访问到本机9010端口的web服务。
附:ZeroTier是一个软件定义网络(SDN)软件,可以免费组建私有网络,当然也可以用来转发服务器请求至本地。
参考链接::
CentOS7搭建ngrok服务器
inconshreveable/ngrok
hteen/ngrok
搭建自己的 Ngrok 服务器, 并与 Nginx 并存
使用Docker部署Ngrok实现内网穿透
Laravel DDNS package,可代替花生壳之类的软件
通过DNSPod API实现动态域名解析
借助dnspod-api定时更新域名解析获取树莓派公网ip
使用Let’s Encrypt生成通配符SSL证书
Letsencrypt使用DNSPOD验证自动更新证书
在 OpenWrt 环境下使用 DnsPod 来实现动态域名解析
利用ssh反向代理以及autossh实现从外网连接内网服务器
How To Configure Nginx with SSL as a Reverse Proxy for Jenkins